Emberiza citrinella

The knowledge of various experts was included in the selection of the bird species.
Profile
- Characteristics
- Male: intense yellow head and underside, upperside rich brown with strong longitudinal stripes, rust-coloured rump, white tail edges.
- Females: duller colouring, underside more heavily striped
- Body length 16-17cm, wingspan 23-29 cm
- Food
- Insects, seeds
- Yellowhammers often forage in cultivated land along fields, ditches and unpaved roads.
- Habitat
- Inhabits transition zones between forest and open landscape
- Especially hedges, e.g. in cultivated land
- Forest edges
- Orchards
- Vineyards
- Best conditions offered by traditional agriculture and horse husbandry
- Inhabits transition zones between forest and open landscape
- Breeding
- The breeding season lasts from April to August. 2 broods per year with 3-5 young are common.
- The young birds leave the nest after 9-14 days.
- Nap nests on the ground or near the ground at the edge of hedges
- Migratory behaviour
- Resident and short-distance migrant
- Distribution
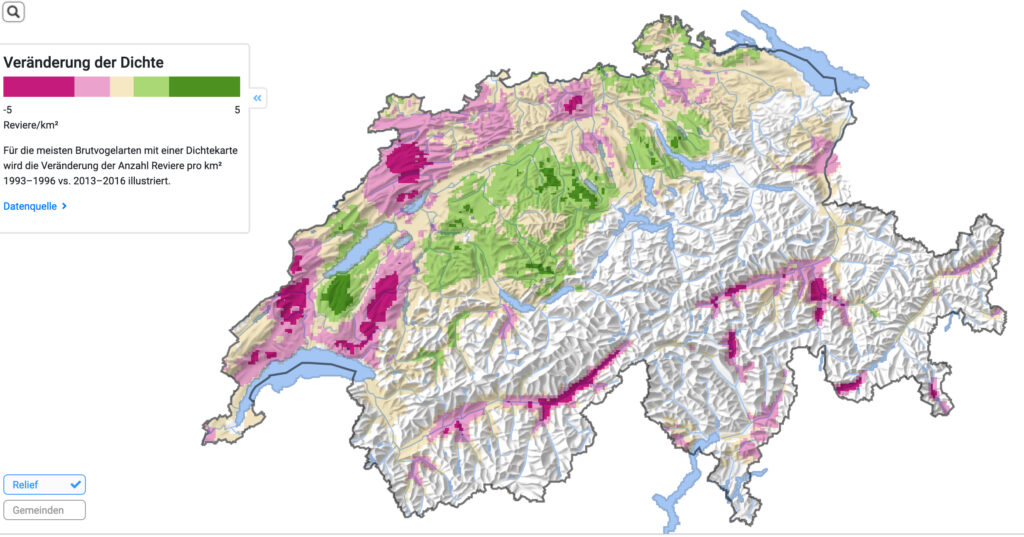
- In Switzerland, the yellowhammer is most common between 400 and 800 metres above sea level in the Central Plateau and Jura and in the central Valais and Lower Engadine.
- At higher altitudes (>700m) the population is declining.
- At lower altitudes, such as in the cantons of Vaud, Bern, Lucerne and Zurich, the population has increased.
- Europe’s most widespread and common bunting
- In Europe as a whole, populations tend to decline.
- Endangerment and conservation measures
- Red List Status (Switzerland): Least concern (LC)
- The intensification of agriculture and land consolidation have reduced the food and habitat availability of the Yellowhammer.
- The population started increasing since the 1980s, when more hedgerows were planted at lower altitudes and additional wildflower strips were created
- The use of pesticides could have a negative impact on the population.
Source: https://www.vogelwarte.ch/de/voegel/voegel-der-schweiz/goldammer

